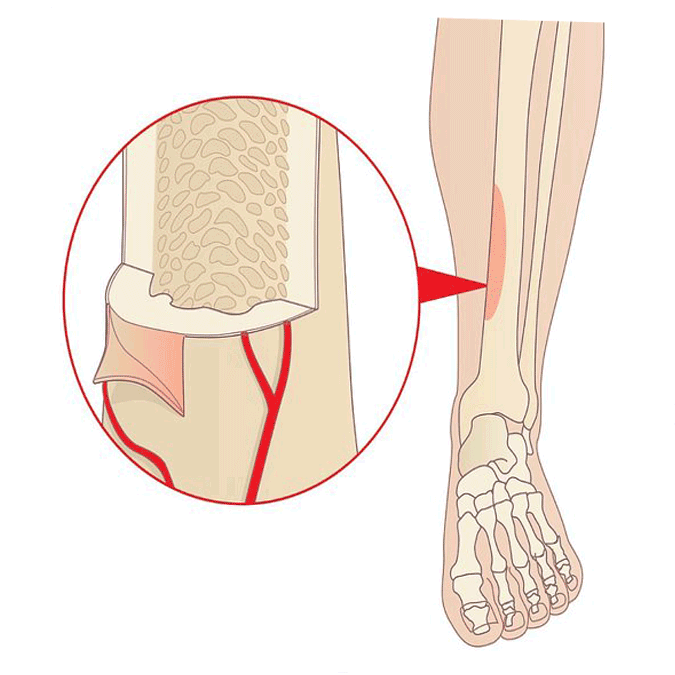
Ankles & Legs
Conditions Treated
Learn more about the ankle and leg conditions our podiatrists commonly treat.
Symptoms may include:
- Mild to severe aching
- Swelling or tenderness
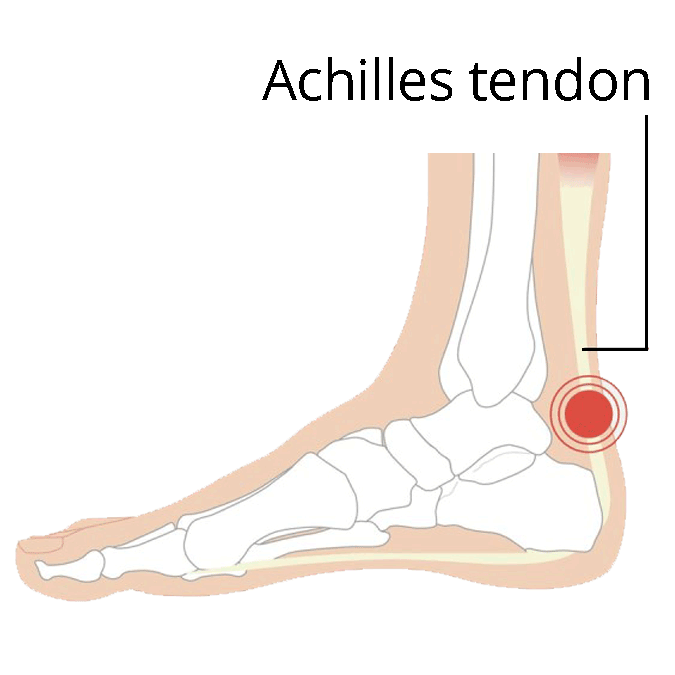
- Pain near the back of your heel
- Stiffness and discomfort after periods of inactivity
- Difficulty bearing weight on the affected leg
Risk factors include:
- Obesity
- Flat feet
- Advanced age
- Taking certain antibiotic drugs
- Wearing ill-fitting or unsupportive workout shoes
It’s important to book an Achilles tendonitis exam if you’re experiencing any symptoms. If left untreated, it can lead to tendon tears that may require surgical repair.
- Physical therapy
- Night splints
- Extracorporeal Pulse Activation Technology (EPAT®)
- Anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Laser therapy
- Stretching exercises
- Custom orthotic inserts
- Heel lifts
If conservative treatments don’t work, your podiatrist may recommend surgery to remove damaged tissues and make any essential repairs.

Find a podiatrist
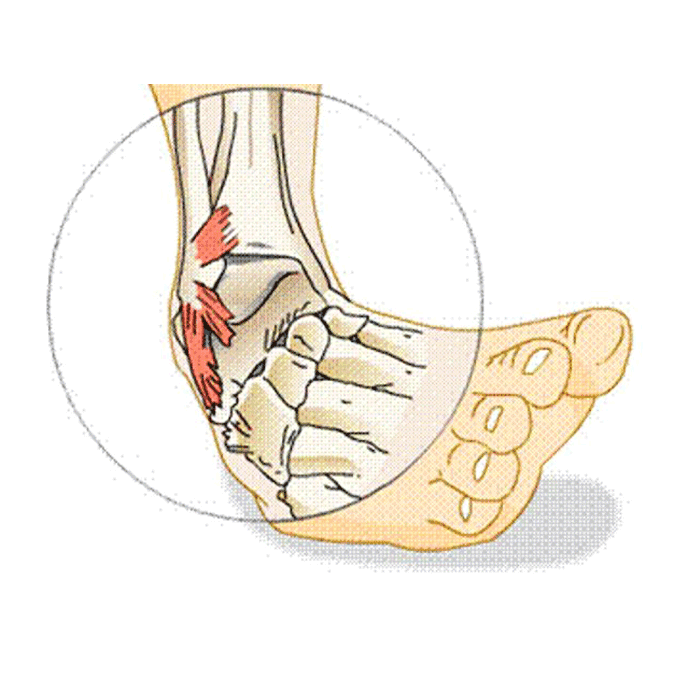
Chronic Ankle Instability Symptoms
- The ankle repeatedly turning, especially while playing sports
- Persistent discomfort and swelling
- Tenderness or pain on the outside of the ankle
- The ankle feeling wobbly or unstable
Other non-surgical treatment options include anti-inflammatory medications and physical therapy to strengthen the ankle.
If these treatment options don’t work, your podiatrist may suggest surgery to repair the damaged ligaments.

Find a podiatrist
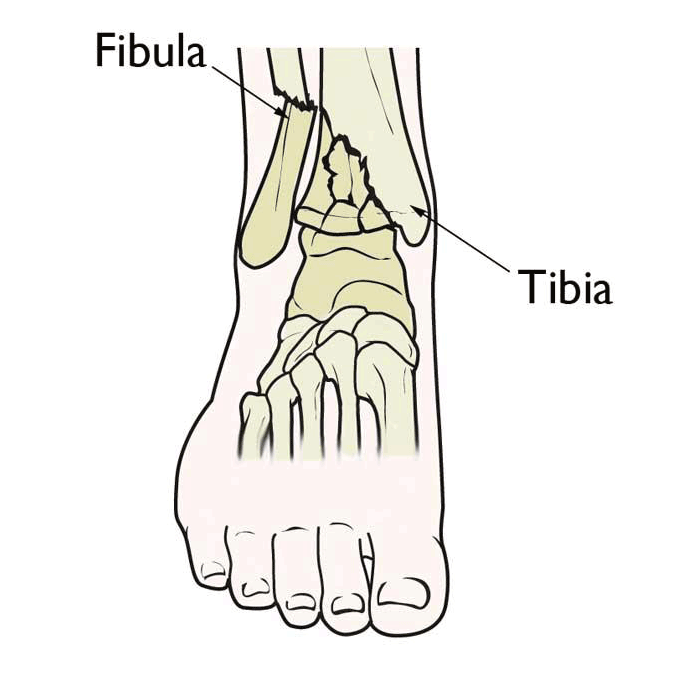
Typical ankle fracture symptoms include:
- Immediate, throbbing pain
- Swelling
- Bruising
- Tenderness to the touch
- Deformity if the fracture is dislocated
- Difficulty bearing weight on the ankle
Your risk of a broken ankle increases if you:
- Participate in high-impact sports
- Use improper technique or sports equipment
- Suddenly increase your activity level
- Work in certain occupations, like at a construction site
- Keep your home messy or poorly lit
- Have certain conditions like decreased bone density
- Stay off your feet, so you do not damage the ankle further
- Keep the injured foot raised to help reduce swelling
- Apply cold packs to decrease swelling and pain
To determine where the fracture is and the severity, your doctor will use a digital X-ray or C.T. scan. If the bones are aligned, and the ankle is stable, a cast or brace is used to keep the bones held in place while they heal. If not, then you may need surgery and physical therapy.
At the first sign of an ankle injury, visit a podiatrist to confirm the diagnosis and begin treatment. If you don’t have a podiatrist, we can help you find one here.

Find a podiatrist
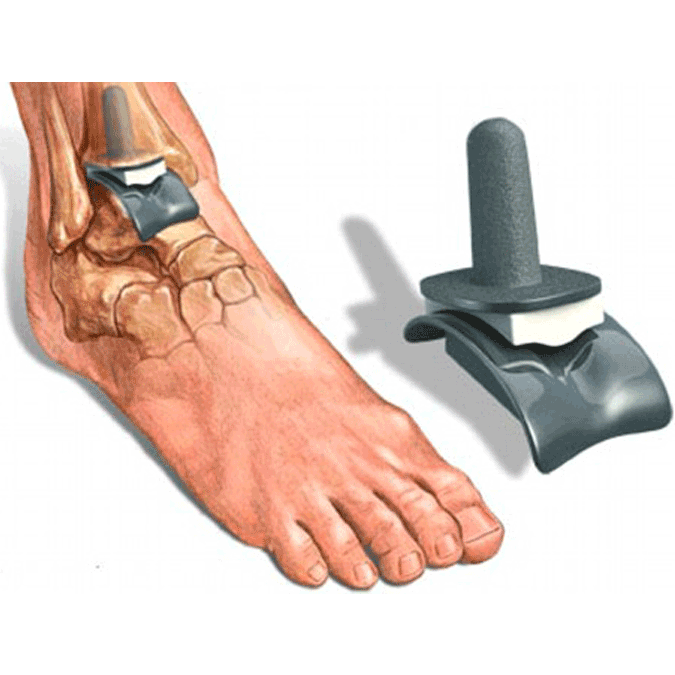
After ankle replacement surgery, you can expect to wear a cast, brace, or splint to prevent the ankle from moving while it heals. Physical therapy will be needed to ensure optimal healing and return of function in your new ankle. Try and be patient (we know that is easier said than done), it may take several months until you can bear weight on the new ankle.
If you’re suffering from chronic, unresolved ankle pain, talk to your doctor. If you don’t have a podiatrist, we can help you find one here.
Shin Splints Risk Factors
While shin splints most frequently affect runners, dancers, and military recruits, it can affect any active individual. This common problem can result from:
- Running on uneven or hard surfaces
- Flat feet or high arches
- Weak ankles, hips, or core muscles
- Shoes that don’t provide proper support
- Suddenly increasing the intensity, frequency, or duration of your exercise
Treatment starts with rest from the activity that is causing the problem—your body needs time to heal. Ice and elastic compression bandages are often recommended to help prevent swelling, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications are used to relieve pain. Your doctor may prescribe orthotics to stabilize the foot and take stress off the leg.
As you recuperate, your doctor may provide exercises to stretch your lower leg muscles. Supportive shoes worn throughout the day can help relieve pain and prevent future shin splints. After you’ve had plenty of time to heal, your doctor will help you develop a plan to return to exercise. Typically, it is suggested to begin at a low intensity and slowly increase training to prevent shin splints from recurring.

Find a podiatrist
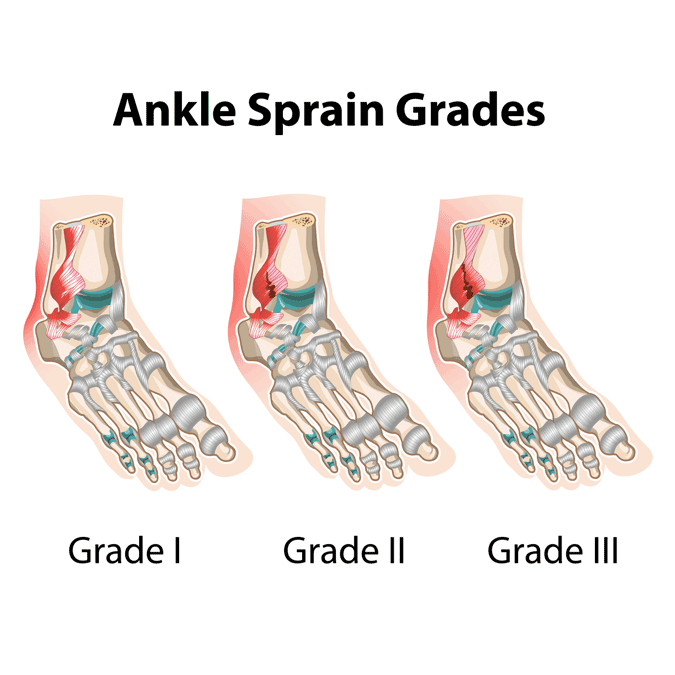
Sprained Ankle Symptoms
- Bruising
- Mild-to-severe pain
- Instability
- A popping sound when the injury occurs
- Swelling
- Limited mobility of the ankle
Those who have had multiple sprains in the past may only experience a wobbly or unsteady ankle. Regardless of the pain level, all sprains need to receive medical attention as soon as possible.
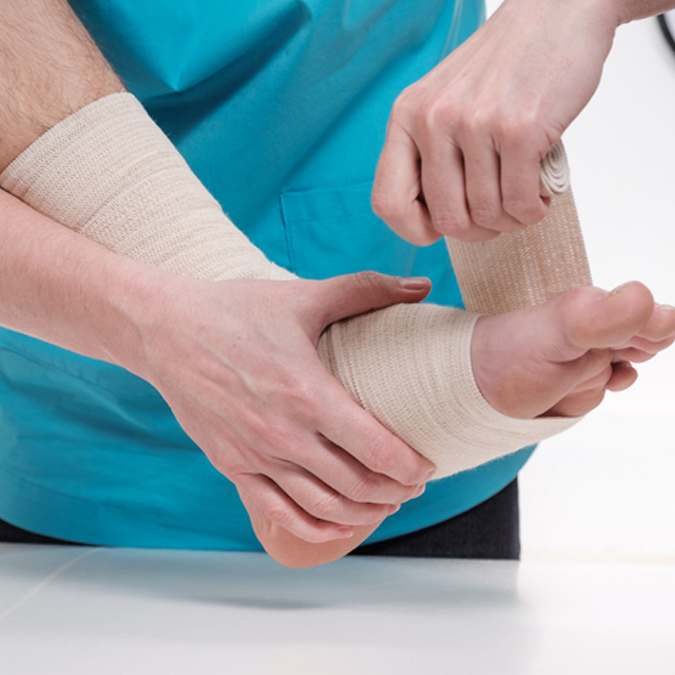
- Resting your ankle
- Elevating it on a pillow when sitting or lying down
- Periodically applying ice to the injury
- Using an elastic bandage to compress your ankle
- A series of stretching exercises to improve the range of motion
- A brace or stirrup for support
- Pain pills, as needed, to alleviate discomfort
Find a podiatrist
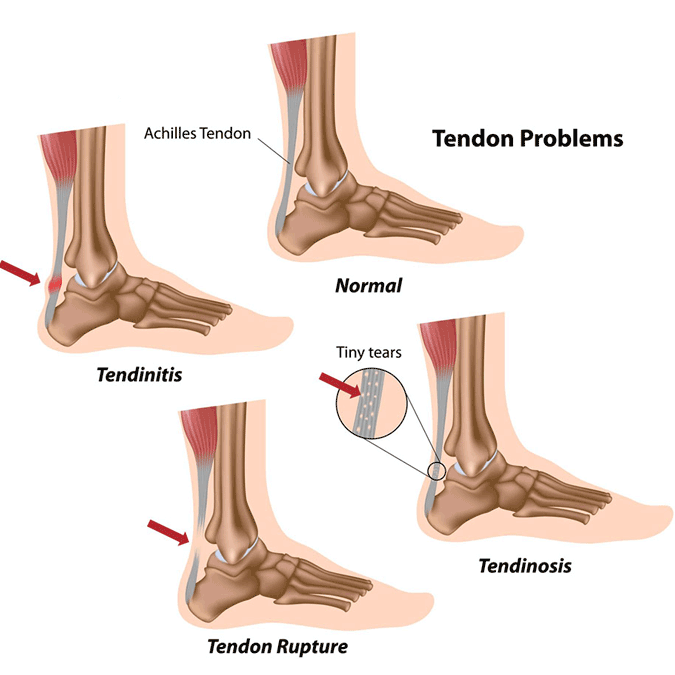
Tendonitis Risk Factors
Many activities can cause tendonitis, including:
- Gardening
- Raking
- Carpentry
- Cleaning the house
- Painting
- Playing tennis
- Golfing
- Skiing
- Throwing and pitching
Incorrect posture or poor conditioning before exercise or playing sports can increase your risk.
Treatment includes rest, immobilization, bracing, orthotics, and physical therapy. When the inflammation leads to a rupture, the tendon may need surgical repair. Stem cell injections or E.P.A.T. pressure waves may also be recommended, depending on the severity.
Find a location near me
Connect