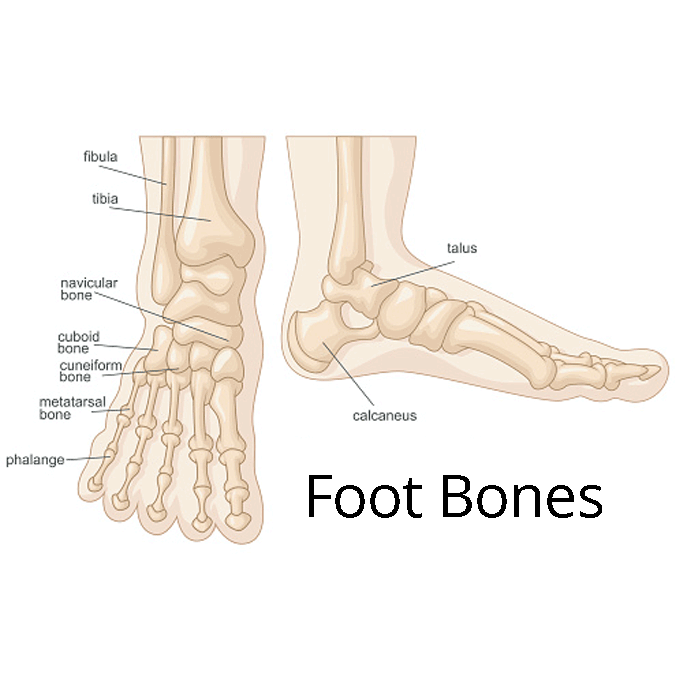
Feet
Conditions Treated
Learn more about some of the most common foot conditions our podiatrists treat.
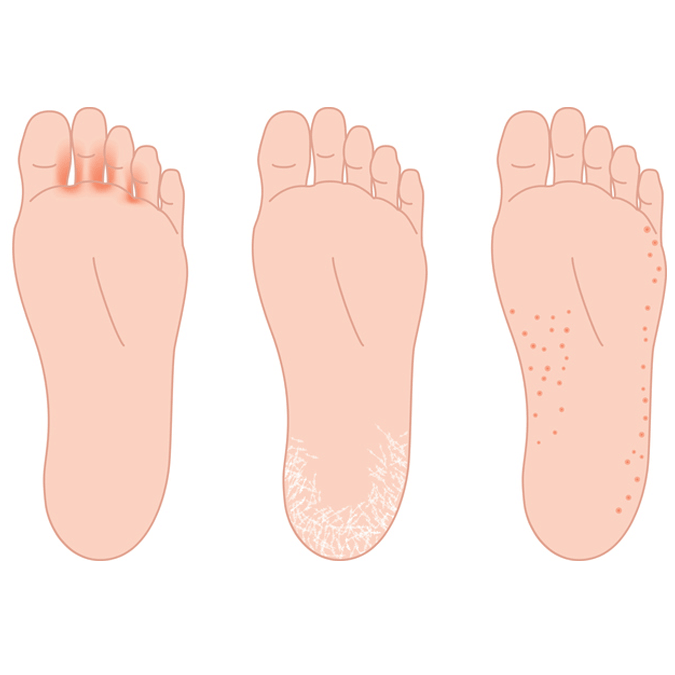
Symptoms may include:
- Itchy, scaly rash between toes
- Small, red blisters
- Ongoing dryness and scaling
- Ulcers or sores
Your risk increases if you:
- Wear closed shoes
- Develop a minor skin or nail injury
- Keep your feet wet for long periods
- Sweat profusely
Athlete’s foot is contagious and can easily be passed through direct contact or contact with items such as shoes, stockings, and shower or pool surfaces.

Find a podiatrist
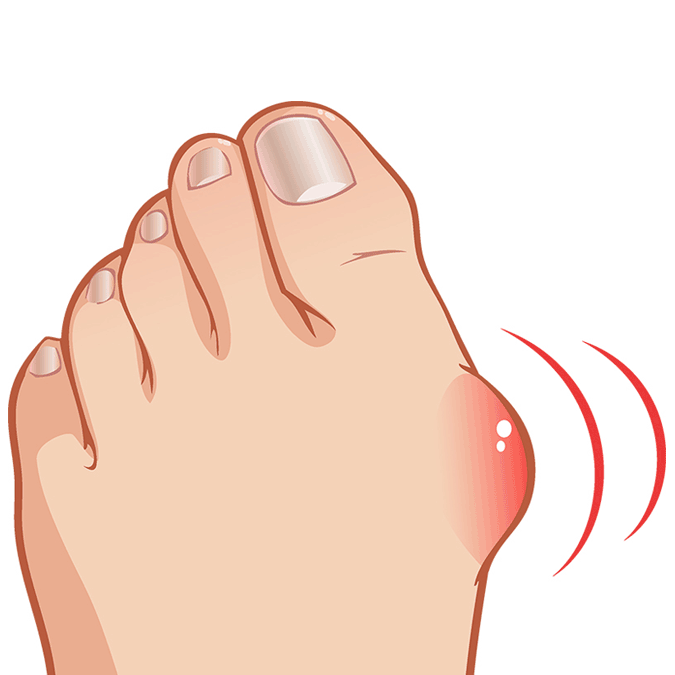
Bunion Symptoms
Other than the bump, symptoms can include swelling, redness, or soreness around the big toe joint. Because the joint at the base of the big toe supports much of your weight when walking, bunions can cause significant and constant pain.
Your doctor may prescribe you an over-the-counter pain reliever and medicine to reduce swelling. Treatment options can include:
- Taping and padding
- Removal of hard calluses
- Dry needling
- Muscle strengthening exercises
- Orthotics (can help reduce pain and prevent further progression of the bunion)
- Injection therapy (usually cortisone is used to reduce levels of pain)
Severe bunions usually require surgery to correct alignment. You will want to talk to your doctor about what you can expect and what recovery will be like.

Find a podiatrist
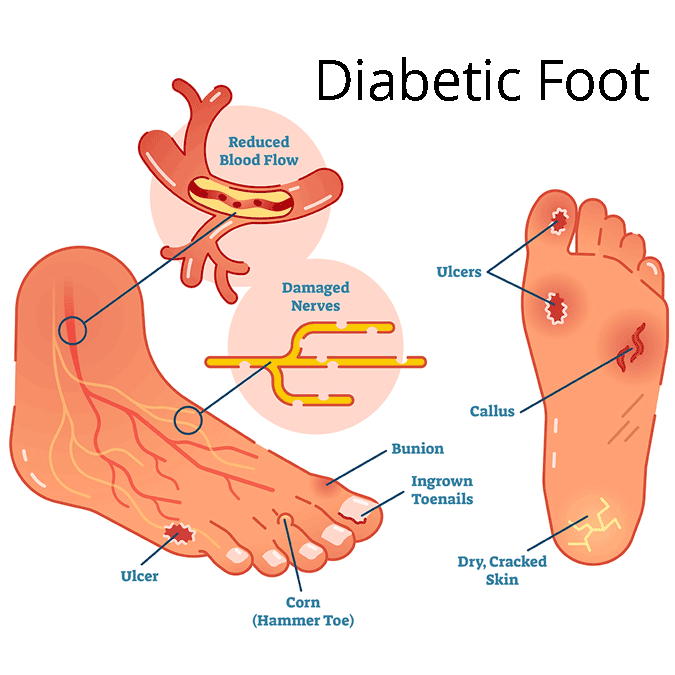
Symptoms
If you have diabetes, contact a doctor if you notice any of these symptoms:
- Skin color changes
- Swelling in the foot or ankle
- Leg pain
- Changes in skin temperature
- Ingrown toenails or toenails infected with fungus
- Open wounds on the feet that are slow to heal
- Calluses
- Corns
- Dry cracks in the skin, particularly around the heel
- Foot odor that won’t go away
Prevention
Some diabetes foot-related problems can be prevented by:
- Controlling your blood sugar
- Not smoking
- Eating healthy
- Checking feet daily for wounds or sores
- Seeking treatment for wounds early
- Keeping feet clean and dry
- Protect from injury and extreme temperatures
- Wearing socks and shoes
- Medications, including antibiotics
- Custom orthotics, inserts, or splints
- Wound care and specialized dressings
- Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy
- Extracorporeal Pulse Activation Technology (EPAT®)
- Radiofrequency therapy
- Surgical debridement or toe removal
Find a podiatrist
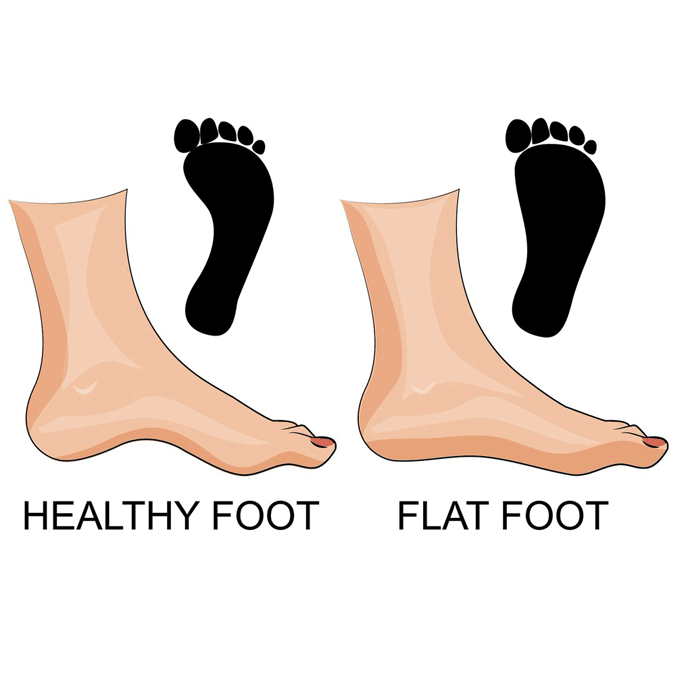
Issues with Flat Feet
Some issues caused by flat feet include:
- Inflammation of soft tissue
- Foot, arch, and leg fatigue
- Heel, foot, and ankle pain
- Knee, hip, and lower back pain
- Rolled-in ankles
- Abnormal walking patterns
- Shin splints
- Bunions
- Hammertoe
- Arthritis
- Plantar fasciitis
- Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction (PTTD)
While not generally anything to worry about, for some, flat feet can lead to chronic foot pain and ankle instability.
- Medications, including antibiotics
- Medications for pain relief and inflammation
- Custom-molded orthotics
- Ankle or foot braces
- Shoe modifications
- Physical therapy
- Fracture boot
Surgery may be needed to correct flat feet if your condition has progressed into a stiff, rigid, or arthritic state. This type of reconstructive foot surgery can repair tendons and restore foot function.
Find a podiatrist
Foot Fracture Risk Factors
Women are much more likely to suffer from fractures than men. In fact, one in two women over 50 will have a fracture in her lifetime.
Other factors that increase your risk of a fracture include:
- Smoking
- Drinking alcohol in excess
- Steroids
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Celiac disease
- Crohn’s disease
- Ulcerative colitis
- Diabetes
Rest, ice, and immobilization are often the treatments. However, surgery is sometimes needed to repair the fracture.
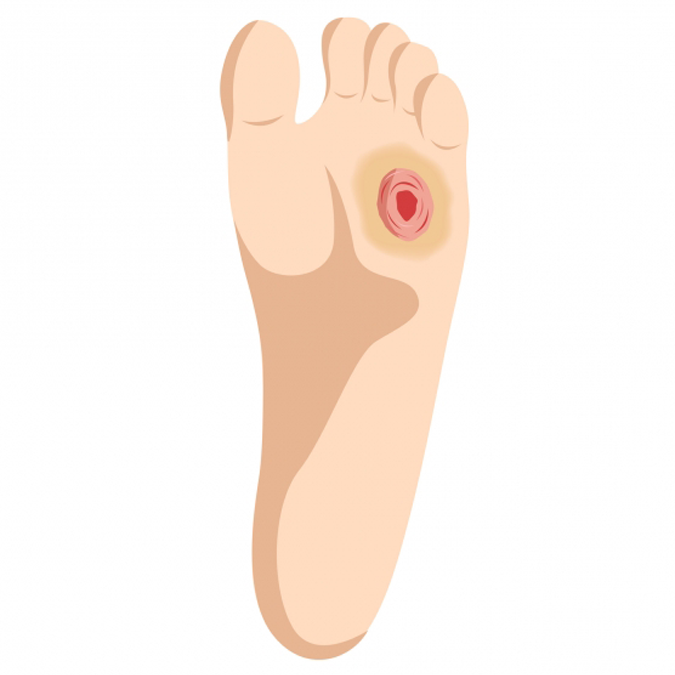
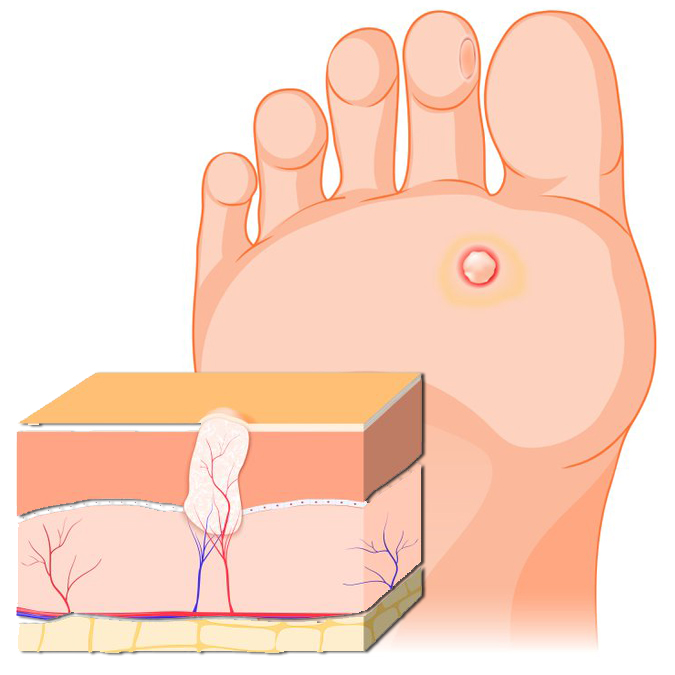
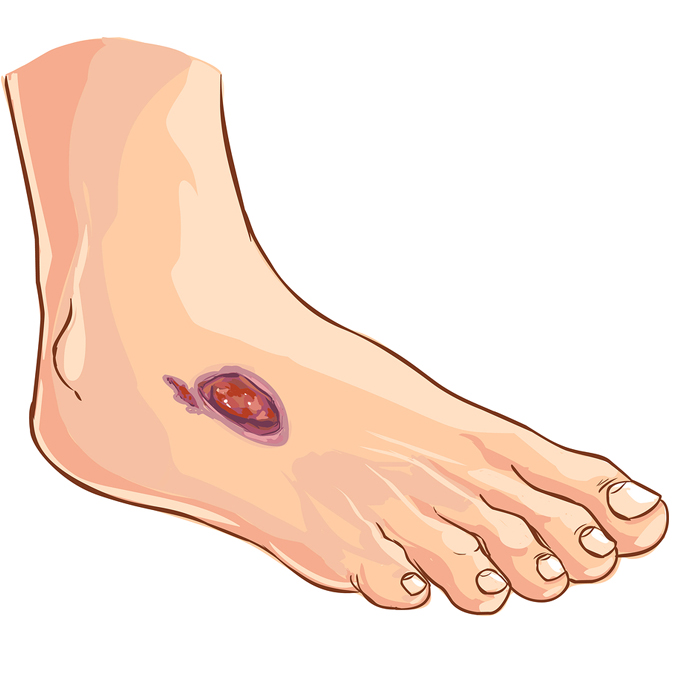
Foot Ulcer Symptoms
Signs of a foot ulcer include:
- Swelling, discoloration, and warmth around the wound.
- Foul-smelling discharge seeping from the wound.
- Pain and firmness when the wound is touched.
- Callused or thickened skin surrounding the ulcer.
- Fever and chills in advanced stages of foot ulcers
Without prompt and proper treatment, a foot ulcer can develop into:
- An abscess (a pocket of pus)
- A spreading infection of the skin and underlying fat (cellulitis)
- A bone infection (osteomyelitis)
- Gangrene. Gangrene is an area of dead, darkened body tissue caused by poor blood flow
- Keeping the wound clean and dry
- Changing the dressing as directed
- Taking prescribed medications as directed
- Drinking plenty of fluid
- Following a healthy diet, as recommended, including plenty of fruits and vegetables
- Exercising regularly, as directed by a physician
- Wearing appropriate shoes
- Wearing compression wraps, if appropriate, as directed
In some case, your doctor will recommend removing the ulcer with a debridement, the removal of dead skin, foreign objects, or infections that may have caused the ulcer. Surgery may be needed to alleviate pressure around the ulcer by shaving down the bone or removing foot deformities such as bunions or hammertoes.

Foot Ulcer Prevention
You can help prevent ulcers by:
- Quit smoking
- Manage your blood pressure
- Control your blood cholesterol and triglyceride levels by making dietary changes and taking medications as prescribed
- Limit your intake of sodium
- Manage your diabetes and other health conditions, if applicable
- Exercise—start a walking program after speaking with your doctor
- Lose weight if you are overweight
- Ask your doctor about aspirin therapy to prevent blood clots
Risks for Nerve Pain
Your risk of developing nerve pain and damage increases due to:
- Trauma or injury
- Drugs or antibiotics
- Tumors
- Diabetes
- Vitamin deficiencies
- Disease
- Excess pressure (tight shoes)
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Prescription pain killers
- Electrical stimulation
- Topical treatments
- Exercise
- Wear comfortable shoes
- Warm baths

Find a podiatrist
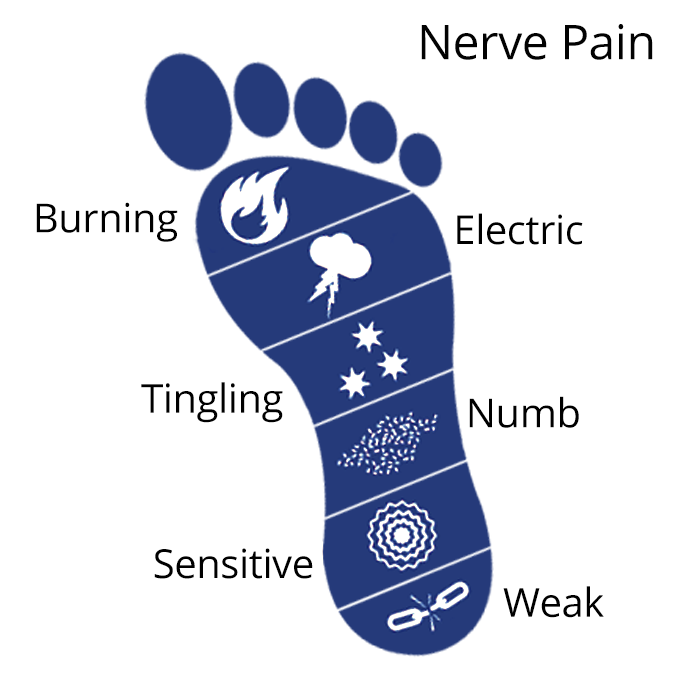
Symptoms may include:
- Burning sensation
- Tingling
- Numbness
- Cramps
Risk factors may include:
- Tight shoes
- High arches or flat feet
- Repeated stress
- Trauma

Find a podiatrist
Neuropathy symptoms include:
- Numbness
- Prickling and tingling sensation
- Throbbing
- Cramps
- Weakness
- Burning pain
- Sharp pain
Neuropathy risk factors include:
- Physical trauma
- Repetitive injury
- Alcohol abuse
- Infection
- Heredity
- Arthritis
- Exposure to toxins
- Metabolic problems
- Diabetes
Prevention tactics like following a healthy diet, exercising, and seeing your podiatrist regularly will help avoid further complications of neuropathy.

- Reduce or eliminate foot pain
- Take pressure off joints
- Increased stability
- Prevent injury
- Prevent future foot problems
Your podiatrist will do a thorough examination to determine which option is best for you. Sometimes, it’s as simple as using an over-the-counter shoe insert. Other times, your pain solutions may call for orthotics.

Osteoarthritis Symptoms
- Pain
- Stiffness
- Swelling
- Loss of flexibility
- A grating sensation
- Tenderness
Osteoarthritis Risk Factors
Your risk of developing osteoarthritis increases due to:
- Repeated stress and use
- Injury
- Abnormal foot mechanics
- Age
- Genetics
- Obesity
- Bone deformities

Find a podiatrist
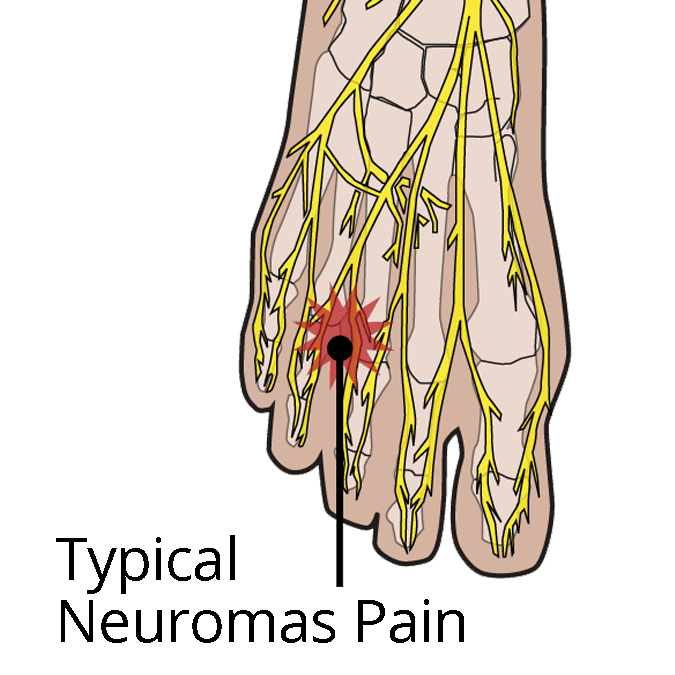
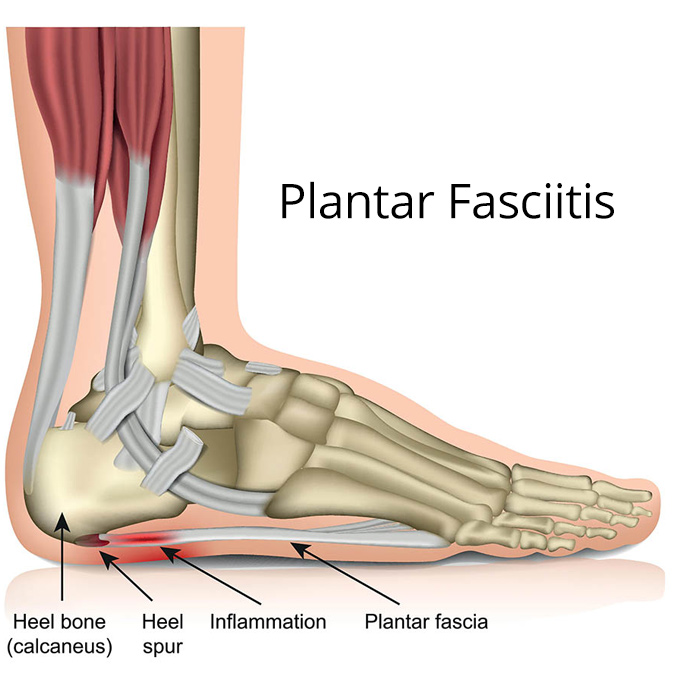
Symptoms may include:
- Sharp, stabbing pain
- Heel tenderness
- Pain after rest or when flexing
- Tingling and burning
Schedule a plantar fasciitis exam if you’re experiencing symptoms. If left untreated, you could develop chronic pain and issues with your knees, hips, and back.
Risk factors include:
- Overexertion from exercise
- Obesity
- Age
- Foot mechanics (flat feet, high arch)
- Ice and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Stretching exercises
- Physical therapy
- Arch supports and orthotics
- Purchasing new shoes
- Night splints
Find a podiatrist
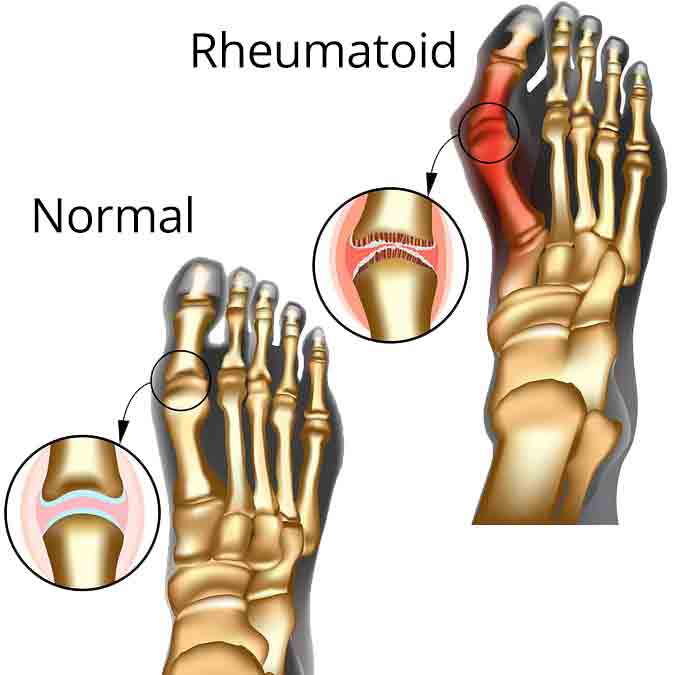
Rheumatoid Arthritis symptoms
- Joint pain and stiffness, swelling, and redness
- Decreased range of motion
- Tenderness around the affected area
- Pain lasts longer than six consecutive months
- Four or more affected joints, including hands and feet
- Physical deformity
- Fatigue
Rheumatoid Arthritis risk factors
- Genetics
- Smoking
- Hormonal
- Exposure to pollution, chemicals, secondhand smoke
- Obesity
- Previous joint injury
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Steroid injections
- Stretching and physical therapy
- Orthotics
Find a podiatrist
Wart Symptoms
As the virus progresses, wart signs and symptoms can include:
- Small, bumpy, or flat growths with a rough or grainy texture
- Pain when walking or standing
- Black dots
Wart Prevention
Follow these steps to prevent warts:
- Wash your hands carefully after touching a wart
- Keep your feet clean and dry
- Avoid walking barefoot around swimming pools and locker rooms

Find a podiatrist
Chronic wound risk factors include:
- Diabetes
- Circulation problems
- Infection
- Arthritis
- Being overweight
- Smoking
- Obesity
Wound care prevention includes:
- Keep hands and feet clean
- Visually inspect feet for signs of blisters, cuts, etc.
- Wear comfortable shoes
- Seek medical attention if your wound worsens
- Keep blood sugar levels under control
- Making sure the wound is constantly clean and bandaged properly
- Wearing compression stocking and bandages to improve blood circulation
- Debridement (cutting down the dead skin and calluses)
- Antibiotics
- Hyperbaric oxygen therapy
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Orthotics
- Regular visits with your podiatrist and other wound care specialists
Find a location near me

Connect