Toes
Conditions Treated
Learn more about how our podiatrists commonly treat toe conditions.
A gout attack can occur suddenly, often waking you up during the night with the sensation that your big toe is on fire. The affected joint is hot, swollen and so tender that even the weight of the sheet on it may seem intolerable.
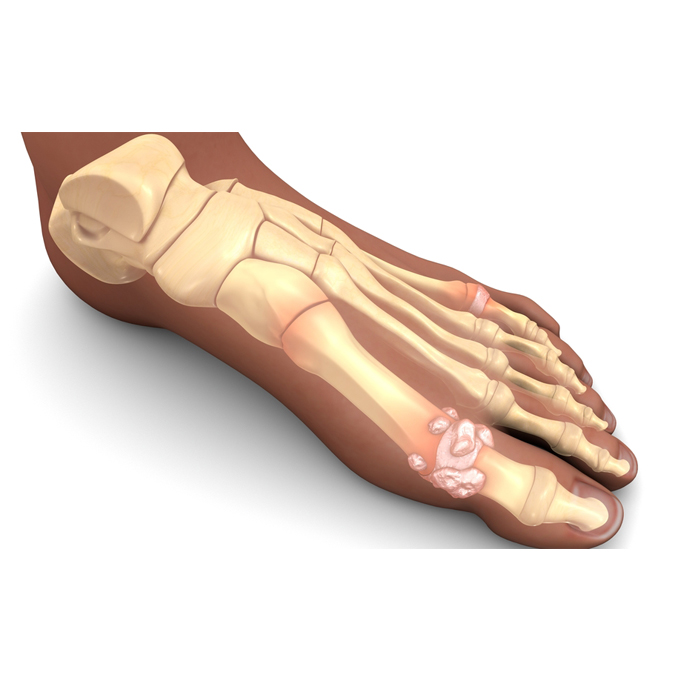
Your Risk of Gout Can Increase Due To:
- Obesity
- Dehydration
- Family history
- Diabetes
- Chemotherapy
- High blood pressure
- Poor kidney function
- Certain medications, including diuretics
Eating large amounts of purine-rich foods, including red meats, organ meats, shellfish, and even alcohol (especially beer), can also trigger increased gout flare-ups.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Uric acid-lowering medications
- Prescription painkillers
- Steroid medications
Find a podiatrist
If you have bunions, it is very likely that you have or will have hammertoes. You’re also at a higher risk when you have diabetes, arthritis, a history of toe or foot injury, or an altered gait or walk.
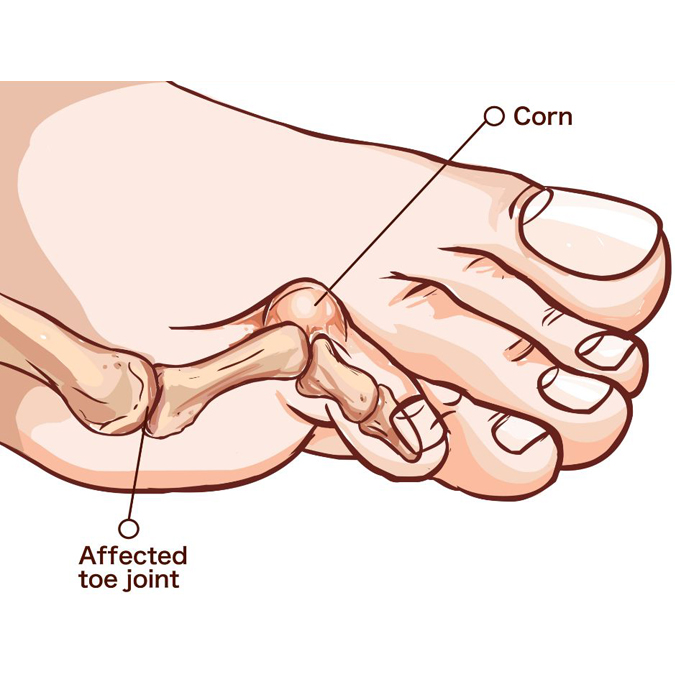
Hammertoe Symptoms
Because hammertoes happen slowly over time, you may not have symptoms initially. Once the condition has progressed, symptoms can include:
- Rigid toe joint
- Limited toe mobility
- Corns or callused skin
- Pain in affected toes and foot
- Swelling in toes and surrounding tissues
Find a podiatrist
One of the most common causes of ingrown toenails is improper toenail trimming—when you cut the nail too short or round the corners. Other causes include wearing shoes that don’t fit properly, genetics, toe/nail trauma, or toenail fungus. Additionally, if you have diabetes or poor circulation, you’re at a higher risk of developing ingrown toenails.
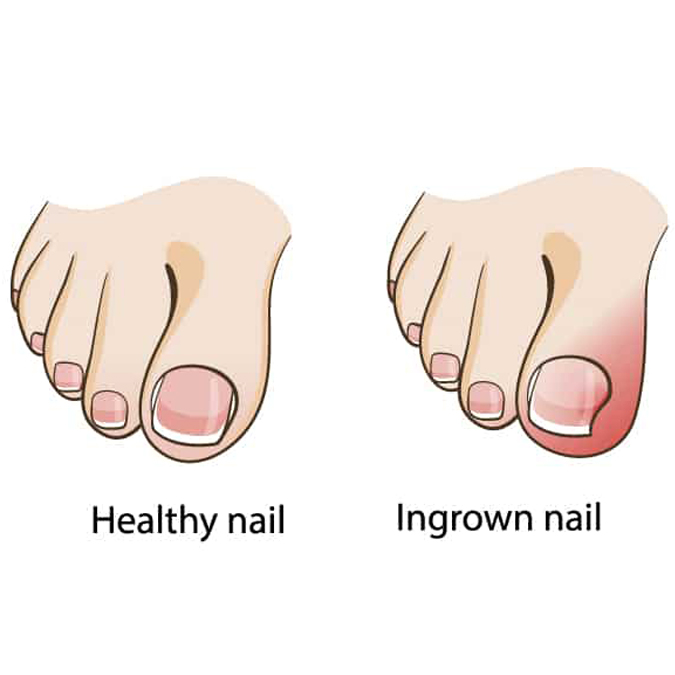
It’s important to recognize ingrown toenail symptoms, which include:
- Redness, heat, and swelling
- Tenderness or throbbing pain
- Drainage from the nail border
- Discoloration of the nail
- Pain when wearing shoes
- Discomfort when bearing weight on the toe
If you are experiencing any of the symptoms, please seek seek treatment, as the severity of an ingrown toenail can progress quickly. Treatment options include oral antibiotics, topical antibiotics, toenail splint, and/or partial/complete removal of the nail—all of which can be performed in the office.
Find a podiatrist
Children and teens can get toenail fungus too. It’s essential to teach them to have good foot hygiene, not to share shoes or socks, and the importance of wearing shoes, especially in public places.
Older adults are at higher risk for a fungal infection due to poor circulation, a less effective immune system, and difficulty keeping their feet dry and clean.
Other factors that place both children and adults at higher risk include:
- Cutting nails/cuticles too short
- Sweating heavily
- Having poor hygiene
- Having an open injury on your foot
- Having diabetes or circulation problems
- Having a history of athlete’s foot or other fungal infection
- Walking barefoot in public areas, like locker rooms, playgrounds, or pools
- Sharing socks or shoes, especially for children and teens
- Having a suppressed immune system
- Using shared pedicure tools that aren’t cleaned properly
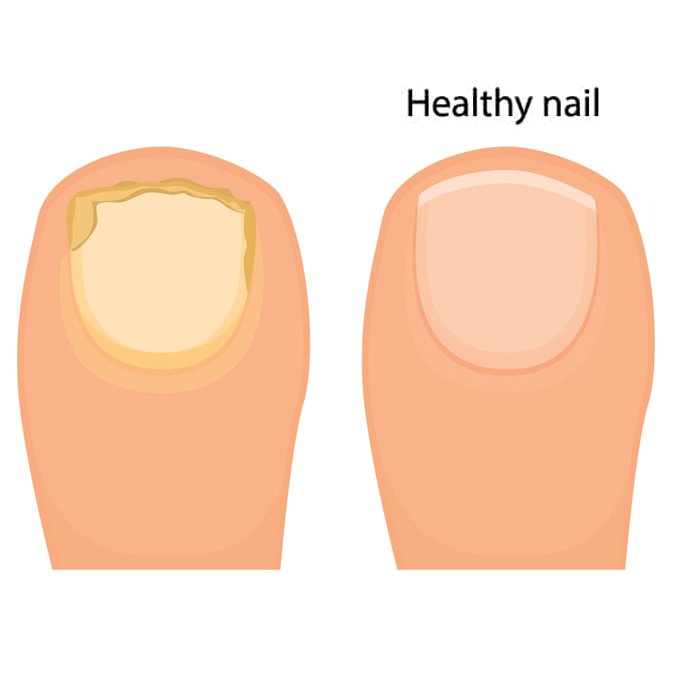
- Discoloration or yellowing
- Brittleness or crumbling
- Thickening or loosening
- Debris under the nail
Toenail fungus can spread to other toenails or other people, so be sure to get treatment, if you suspect you may have symptoms. Treatments include laser therapy, antifungal soap, medications, and nail debridement. Severe and recurrent cases may require surgical removal of the nail.
Find a location near me
Connect
